Periodontitis is generally called as gum disease or periodontal disease. It begins with bacterial growth in your mouth and may end with tooth loss due to destruction of the tissue that surrounds your teeth. It needs proper and timely treatment. Usually people confuse the Gingivitis with periodontitis but there is difference between two.
Gingivitis is basically gum inflammation but it usually precedes periodontitis which is gum disease. But its not necessary that all gingivitis progresses to periodontitis. In the early stage of gingivitis, bacteria in plaque buildup, causing the gums to become inflamed and to easily bleed during tooth brushing. Although the gums may be irritated, the teeth are still firmly planted in their sockets. No irreversible bone or other tissue damage has occurred at this stage.
Gum disease can be reversed in nearly all cases when proper plaque control is practiced. Proper plaque control consists of professional cleanings at least twice a year and daily brushing and flossing. Brushing eliminates plaque from the surfaces of the teeth that can be reached while flossing removes food particles and plaque from in between the teeth and under the gum line. Antibacterial mouth rinses can reduce bacteria that cause plaque and gum disease, according to the American Dental Association.
Periodontal disease Cure, Causes and Signs
Below you can find all relevant information about Periodontal disease including its cure, causes and signs. So keep reading.
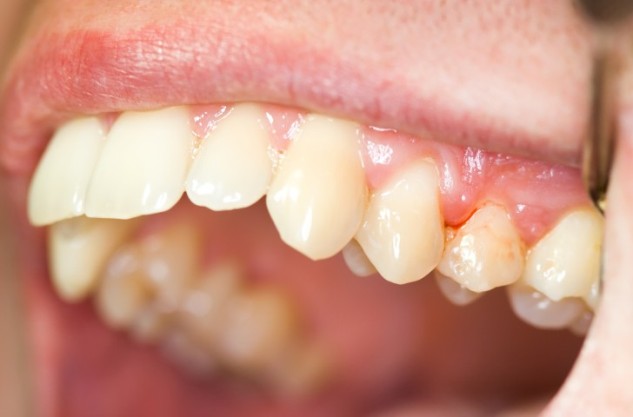
Signs of Periodontal disease
As mentioned above that sometimes your inflammatory gums may lead to periodontitis so it can also be taken as a sign of gum disease if your gums have inflammation. It is seen that untreated gingivitive advance to periodontitis. In a person with periodontitis, the inner layer of the gum and bone pull away from the teeth and form pockets. These small spaces between teeth and gums collect debris and can become infected.
The body’s immune system fights the bacteria as the plaque spreads and grows below the gum line.Bacteria in plaque as well as the body’s “good” enzymes involved in fighting infections start to break down the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place. As the disease progresses, the pockets deepen and more gum tissue and bone are destroyed. When this happens, teeth are no longer anchored in place, they become loose, and tooth loss occurs. Gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults.
Causes of Periodontal disease
There are number of causes that may lead towards Periodontal disease such as:
- Plaque is the primary cause of gum disease.
- Hormonal changes can be a reason behind Periodontal disease . Like hormonal changes during pregnancy, puberty, menopause, and monthly menstruation, make gums more sensitive, which makes it easier for gingivitis to develop.
- Illnesses can be another reason that may affect the condition of your gums. This includes diseases such as cancer or HIV that interfere with the immune system. Diabetes affects the body’s ability to use blood sugar, patients with this disease are at higher risk of developing infections, including periodontal disease and cavities.
- Medications can also affect oral health. Mostly medicine effects the flow of saliva, which has a protective effect on teeth and gums.
- Smoking can also lead to gum diseases as it make harder for gum tissue to repair itself.
- Poor oral hygiene habits such as not brushing and flossing on a daily basis, make it easier for gingivitis to develop.
- Family history of dental disease can be a contributing factor for the development of gingivitis.
Cure of Periodontal disease
Gum disease treatment is designed to do reattachment of healthy gums to teeth; reduce swelling as well as the depth of pockets. Another goal of this treatment is to minimize the risk of infection and to stop disease progression.
- Treatment options depend on the stage of disease and your overall health.
- Treatment may include nonsurgical therapies that control bacterial growth to surgery to restore supportive tissues.
- Surgical treatment may be needed in more severe cases of periodontal disease that do not respond adequately to non-surgical initial therapy .
How to prevent Periodontal disease
Following things are important to keep in mind if you want to keep your gums healthy:
- Proper and regular brushing.
- Use a good, soft toothbrush and healthy toothpaste. Avoid conventional toothpastes, buy a good natural toothpaste.
- Flossing is must.
- Don’t smoke.
- Eat a healthy, nutrient dense diet.
- Take whole food supplements, paying special attention to your need for vitamin D, vitamin C, and B vitamins
- Help heal your gums with natural solutions that promote gum health.
- Chew raw garlic.
- Practice oil pulling.


